LASER CLEANING OF METALS
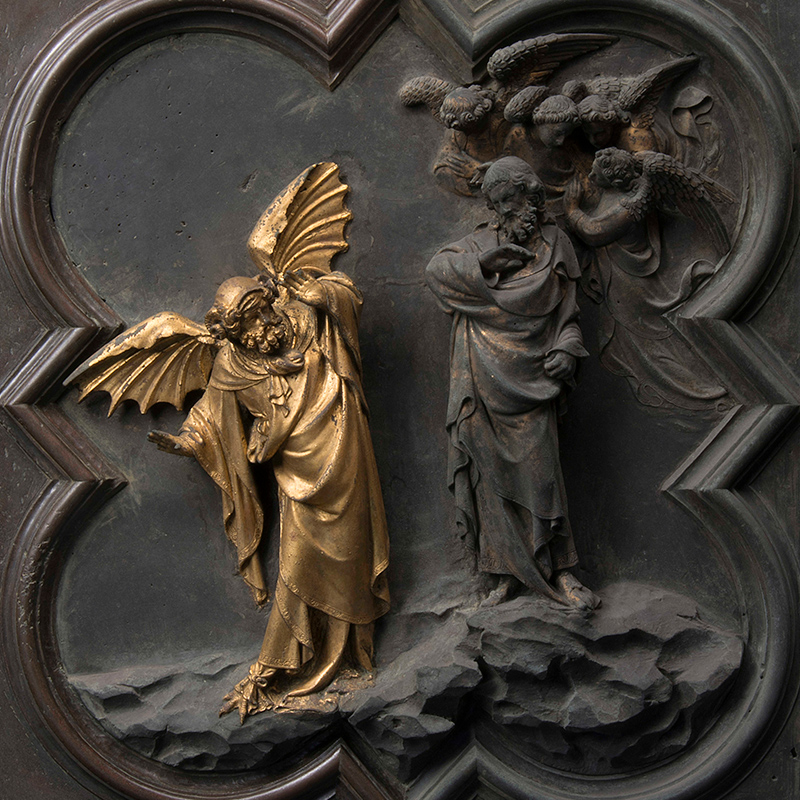
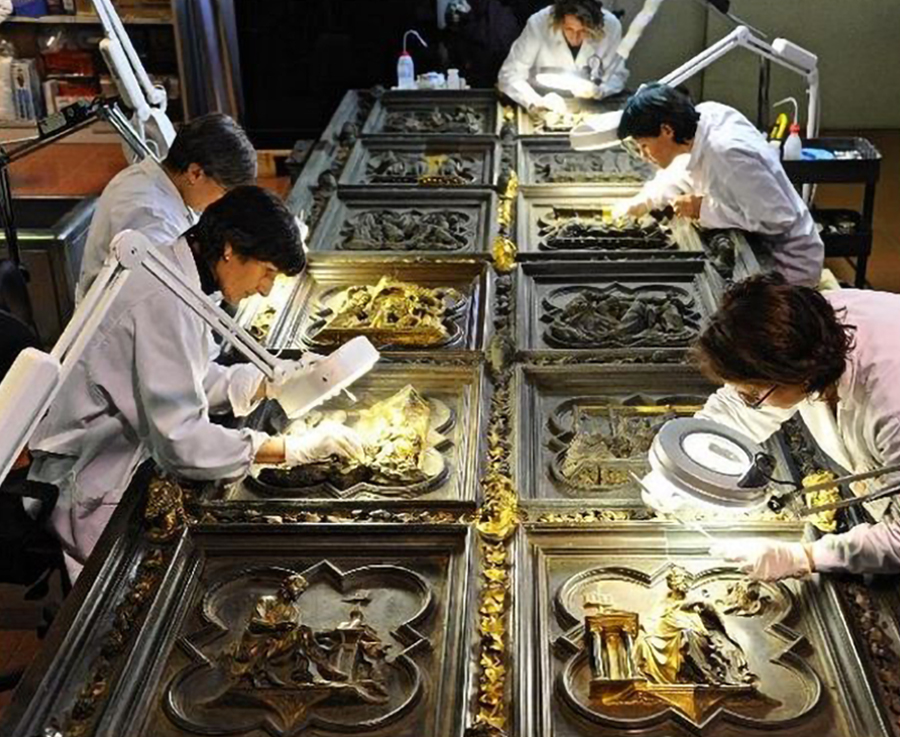
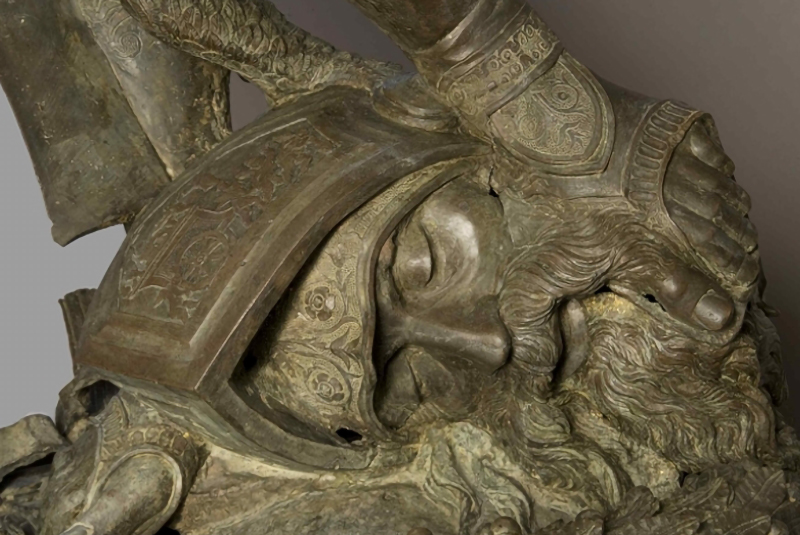
When it comes to artefacts of artistic and archaeological interest, the laser can be used for the conservation of a wide variety of metals. A few years ago, a particular type of laser was developed by National Research Centers to remove oxidations and superimposed patinas from gilded bronze surfaces. From these first experiences the applications have spread: lasers have been employed also in the restoration of large monumental complexes directly on the bronze and copper surfaces, allowing to preserve the original patinas as the details of the workmanship.